The Basics of FDM 3D Printing Materials
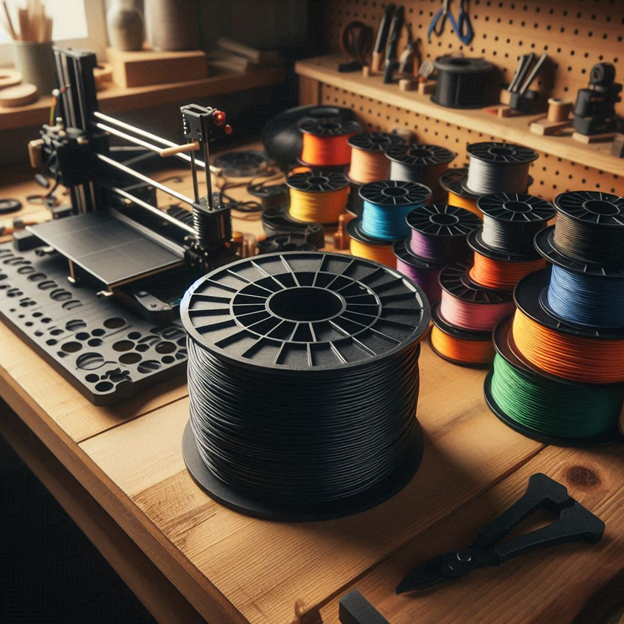
When it comes to 3D printing, the material you choose is just as important as the printer itself. Filament is the thermoplastic feedstock used in fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printers. It is a continuous slender plastic thread spooled into a reel, with diameters ranging from 1.75 mm to 2.85 mm. Filament comes in various types, each with its own unique properties.
3D printers use different mechanisms to extrude the filament and build up layers to create your final model.
How Filament Choice Impacts Your 3D Printing Project
The choice of 3D printing filament can have a significant impact on the outcome of your 3D printing project. Different filaments have different properties, such as strength, flexibility, and temperature resistance. Understanding these properties and how they relate to your project is crucial for achieving the desired results.
For example, if you’re printing functional parts that require strength and durability, ABS or PETG would be suitable choices. On the other hand, if you’re creating decorative or artistic pieces, PLA or specialty filaments like wood or even metal may be more appropriate.
Exploring Just a Few Types of Available 3D Printer Filaments
PLA (Polylactic Acid)
PLA is one of the most popular filaments for 3D printing. It is a biodegradable and environmentally friendly filament that is derived from renewable resources such as cornstarch or sugarcane. PLA is easy to print with and offers good dimensional accuracy. It is known for its vibrant colors and smooth surface finish. PLA is commonly used for prototyping, hobbyist projects, and decorative prints. It is compatible with most commercially available FDM printers and can be printed at lower temperatures compared to other filaments.
 ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
ABS is a popular filament known for its durability and impact resistance. It has a higher melting temperature compared to PLA, making it suitable for functional parts that require strength and toughness. ABS is commonly used in applications such as automotive parts, electronic enclosures, and industrial prototypes. It can be challenging to print with due to its tendency to warp and emit strong fumes during printing. However, with proper printer settings and a heated bed, ABS can produce high-quality prints with excellent mechanical properties.
PET (Polyethylene terephthalate)
PET is a popular 3D printing filament known for its strength and flexibility. Its durability and impact resistance ensure long-lasting printed objects, while its flexibility allows for complex shapes without cracking. Additionally, it offers excellent chemical resistance and is food-safe, making it suitable for kitchen items. PET is easy to print with a lower risk of warping and can be used on most standard 3D printers. Being recyclable, it also provides an eco-friendly option for various 3D printing projects.
 PETG (Polyethylene terephthalate glycol)
PETG (Polyethylene terephthalate glycol)
PETG is a variation of PET that offers improved impact resistance and chemical resistance. It’s a versatile filament known for its balance of strength, flexibility, and temperature resistance. It is commonly used for functional parts, mechanical components, and consumer products that require durability and impact resistance. PETG has excellent layer adhesion, making it ideal for strong and durable prints. Additionally, it is FDA-approved for food contact, making it a popular choice for printing kitchen utensils and containers.
TPU (Thermoplastic polyurethane)
TPU is a flexible filament that is widely used for creating elastic parts and prototypes. It offers excellent resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and oils, making it suitable for applications that require flexibility and durability. TPU is commonly used in industries such as automotive, footwear, and prosthetics. It can be printed with ease on most FDM printers and does not require a heated bed. TPU is available in various shore hardness ratings, allowing for different levels of flexibility and elasticity in prints.
Specialized 3D Printing Filaments
In addition to the common filaments used in 3D printing, there are specialized filaments that offer unique properties for specific applications. These filaments are often infused with different materials to enhance their properties. Some examples of specialized filaments include carbon fiber-infused filaments, which offer high strength and rigidity, and metal-infused filaments, which allow for the printing of metal-like objects. These specialized filaments are commonly used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and jewelry.
 Onyx by Markforged: High Performance Carbon Fiber
Onyx by Markforged: High Performance Carbon Fiber
Onyx is a high-performance carbon fiber filament developed by Markforged. It combines the strength and rigidity of carbon fiber with the ease of printing with nylon. Onyx is known for its excellent dimensional stability, high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to heat and chemicals. It is commonly used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and defense for applications that require lightweight yet strong parts. Onyx can be printed on Markforged 3D printers, which are specifically designed to handle the unique properties of this filament.
Metal 3D Printing: Stainless Steel, Copper, and more
3D printing with metal filaments allows for the creation of metal-like objects without the need for traditional metalworking processes. These filaments are composed of a mixture of metal powder and a binding agent. After printing, the object can be further processed to remove the binding agent and sinter the metal particles together, resulting in a solid metal part.
While an expensive and infrastructure-heavy investment, 3D printing with metal filaments offers the ability to create complex geometries and customized metal parts with good mechanical properties.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Filament
When choosing a filament for your 3D printing project, consider factors like strength, durability, flexibility, temperature resistance, and printer compatibility. Filaments such as ABS, PETG, or carbon fiber are suitable for strength, while TPU works well for flexibility. For high temperatures, consider polycarbonate. Always remember to check compatibility with your printer’s settings!
Assessing the Strength and Durability Needs of Your Project
When selecting a filament for your 3D printing project, it is essential to assess the strength and durability needs of your project. Consider the intended use of the printed object and the level of stress it will be subjected to. If you require high strength and impact resistance, filaments like ABS, PETG, or carbon fiber-infused filaments may be suitable. These filaments offer excellent mechanical properties and can withstand heavy loads and impacts.
Considering Flexibility and Elasticity for Functional Parts
For functional parts that require flexibility and elasticity, it is important to consider filaments that can meet these requirements. TPU is a popular choice for flexible prints. It offers excellent flexibility and resilience, making it ideal for applications such as phone cases, prosthetics, and wearables. TPE (Thermoplastic elastomer) is another flexible filament that provides a soft and rubber-like texture. It is commonly used for creating gaskets, seals, and other parts that require high flexibility.
Temperature and Environmental Resistance
Temperature and environmental resistance are important considerations when selecting a 3 D printing filament. Different filaments have different temperature ranges at which they perform optimally. For example, PLA can be printed at relatively low temperatures (180-230°C) and is suitable for most everyday applications. On the other hand, filaments like polycarbonate (PC) and polyetherimide (PEI) have higher temperature resistance and can withstand elevated temperatures (up to 340-380°C). These filaments are commonly used in applications that require exceptional heat resistance, such as aerospace components and automotive parts.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Cost-effectiveness and availability are key factors when selecting 3D printing filament. PLA is popular for being affordable and widely available, as well as eco-friendly. PETG is valued for its strength and durability with better impact resistance than PLA. While PLA and PETG are cost-effective and common, ABS and Nylon may be pricier but offer unique strengths. ABS provides high strength and temperature resistance for functional parts, while Nylon offers flexibility and durability for specialized applications like gears. Finding this balance depends heavily on the user, projects, and printing frequency.
Consider how you prefer to source your materials. Are you more comfortable dealing with a consistent supplier, or are the readily available 3D printing filaments on Amazon enough for your needs? It’s important to consider the specific requirements of your project and budget constraints when selecting a 3D printing filament. By balancing cost-effectiveness and availability, you can ensure that you choose the best filament for your 3D printing needs.
Balancing Quality with Budget Constraints
Similarly, choosing the right 3D printing filament involves balancing quality and budget. High-quality filaments offer superior performance but come at a higher cost. Research and comparing brands can help find affordable options with satisfactory results. Reading reviews and seeking recommendations can identify cost-effective choices. Experimenting with different types of filaments can help strike a balance between quality and budget based on project requirements.
Application-Specific Recommendations
Different 3D printing applications require different 3D printing filament types to achieve optimal results. By selecting the right material for your specific application, you can ensure that your 3D prints meet the desired functionality and performance requirements.
Prototyping with Precision: Choosing the Right Material
When it comes to precision prototyping, choosing the right 3D printing filament is crucial to achieve accurate and detailed prints. Different materials offer varying levels of precision and surface finish.
PLA (Polylactic Acid) is a popular choice for precise prototyping due to its low shrinkage and excellent dimensional accuracy. It provides smooth and clean prints, making it ideal for visual models and product prototypes. Additionally, PLA is easy to print with and offers a wide range of colors to choose from.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is another material suitable for precision prototyping. It offers better temperature resistance and durability compared to PLA, making it suitable for functional prototypes that require strength and impact resistance.
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol) is also a good option for precision prototyping. It offers a balance of strength, flexibility, and dimensional stability, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
By selecting the right material for precision prototyping, you can ensure that your prints accurately represent your design and meet your quality expectations.
Functional Parts and Mechanical Components: What Works Best?
When it comes to printing functional parts and mechanical components, choosing the right filament is essential to ensure durability and performance. Different materials offer varying mechanical properties and characteristics.
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) is an excellent choice for parts that require flexibility and resilience. It offers high elasticity and impact resistance, making it suitable for gaskets, seals, and other flexible components.
Nylon is known for its exceptional strength and toughness, making it ideal for functional parts that require durability and high load-bearing capabilities. It also offers good chemical resistance, making it suitable for applications in harsh environments.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a versatile material that provides a balance of strength, impact and temperature resistance. It is commonly used for functional parts in various industries, including automotive and aerospace.
By choosing the right filament for functional parts and mechanical components, you can ensure that your 3D prints meet the required performance standards and withstand the intended applications.